Africa 1677
Nicolaes Visscher
€ 1.650
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De Jonge
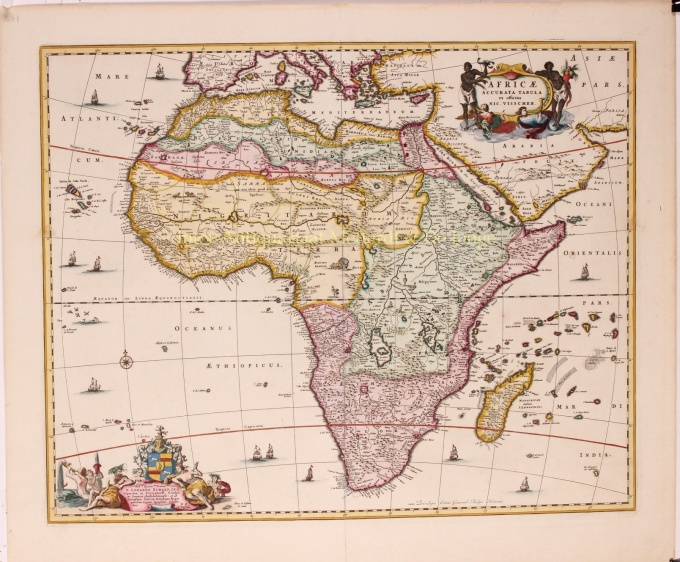
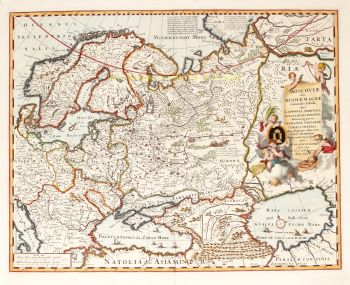
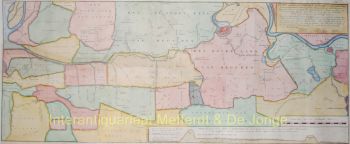
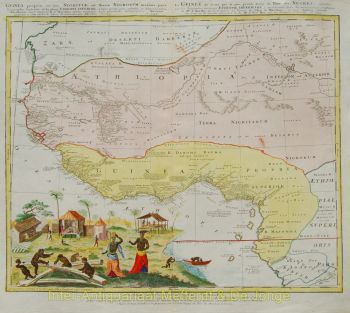
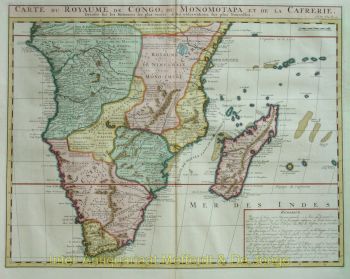
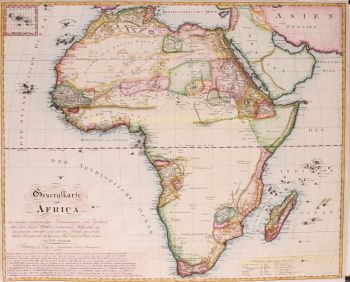
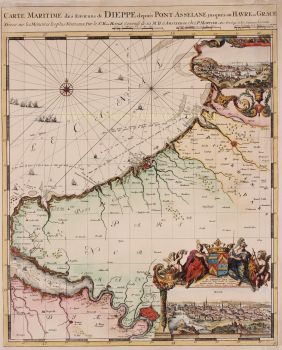
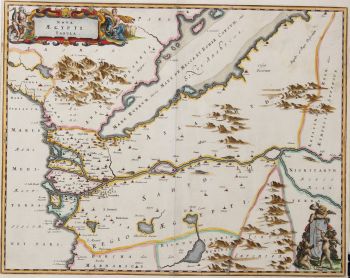
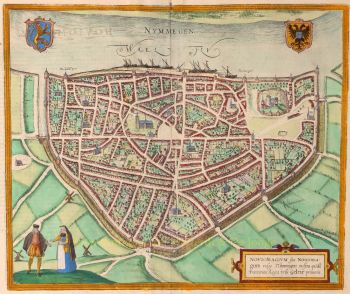
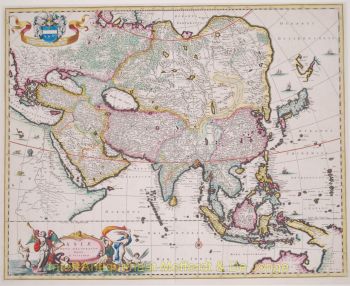
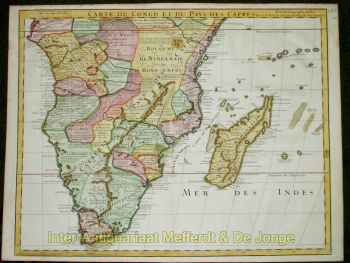
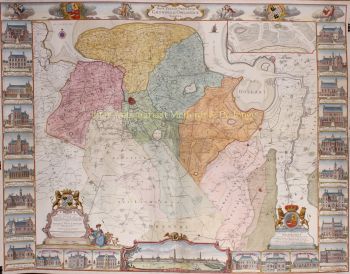
- A proposito di opere d'arte“Africae Accurata Tabula”, copper engraving with original hand colouring by Nicolaes Visscher made in 1658, here in its second state published c. 1677. Size: 43,7 x 54,6 cm. The map illustrates the European view of Africa at the end of the 17th Century, filled with mythical towns, rivers, and mountains and continues to reflect the Ptolemaic view of Africa. Claudius Ptolemy imagined the Nile emanating from two massive lakes in south-central Africa, fed from springs in the imaginary Lunae Montes [the Mountains of the Moon]. The Niger River is shown as well - springing from a Niger Lacus in the general vicinity of the Congo, flowing north and then westward to empty near the actual location of the Gambia River. (The Niger, whose full course was not understood by Europeans until well into the 19th century, actually begins in West Africa well south of The Gambia, and then flows eastwards, emptying into the gulf of Guinea.) To prepare for this map, Visscher turned to the common model of the period which was Willem Blaeu’s 1608 wall map. Like Blaeu, Visscher shows a common source for the Cuama and Spirito Santo Rivers of the Zambese River originating in Sacaf Lacus in Southern Africa. The general outline of Africa is surprisingly modern in appearance. Of special note is the much greater detail that Visscher provides along the South African coastline. The first Dutch settlement under Jan van Riebeeck at the Cape of Good Hope had occurred in 1652, and it is likely that Visscher wanted to show this information on his map. Visscher introduces a number of Dutch names mixed with older Portuguese names. Among these names are Tafel Bay [Table Bay], Tafel Berg [Table Mountain], Robben Eyl [Robben Island], and Schorre hoeck (inland from C. das Aguillas [Cape Agulhas], the southern-most point in Africa). From about 1631 and prior to the issuance of this map, the Visscher publishing family used a a map of Arica of 1614 by Pieter van den Keere for their atlases. This map was used in a number of atlases produced by Nicolaas Visscher up to 1679, when upon his death, his son Nicolaas Visscher II began issuing his own Atlas Minor, using his father’s plate. The second state of the map has been found in atlases dated as late as 1696. The title cartouche in the upper right is surrounded by two Africans, one holding a scorpion and the other a cornucopia. The lower left of the map has an elaborate dedication to Gerard Schaep (1581-1655), a cartouche with Neptune, mermaids and a sea monster bears his coat of arms. Schaep was a mayor of Amsterdam sent by the States General of the Netherlands to London on 27 December 1651 as part of an embassy. The intention of the embassy was to convince the English to withdraw the Navigation Act and to negotiate a new commerce treaty. There were not successful and the First Anglo-Dutch Was resulted. It can be assumed that Visscher’s dedication was to acknowledge this statesman upon his death. The fish being waved about in the cartouche, has little to do with Gerard Schaep and more to do with the mapmaker. Visscher’s name translates literally to “Fisher”, and thus fishermen and fish alike adorn many of the mapmaking family’s works. Price: Euro 1.650,-
- A proposito di opere artista
Nicolaes era l'unico figlio di Claes Jansz. Pescatore. È anche conosciuto con i nomi: Nicolaas o Claes Claesz. Dopo anni di lavoro per il padre nell'azienda, gli succedette dopo la sua morte nel 1652. Nel 1662 fu ammesso alla corporazione dei librai di Amsterdam e nel 1677 Nicolaes, ormai rispettato editore, ricevette un brevetto di 15 anni dagli stati dell'Olanda e della Frisia occidentale per la stampa e la pubblicazione di mappe. Morì due anni dopo e fu sepolto nella stessa cappella del padre.
Le edizioni Atlas di Nicolaes I includevano:
"Atlas Contractus Orbis Terrarum" del 1657.
“Germania Inferiore” del 1663.
"Atlante Minore" del 1675.
Gli atlanti di Visscher venivano spesso compilati secondo i desideri degli acquirenti (il cosiddetto Atlas Contractus). Generalmente non contengono testo, solo a volte un indice stampato. Sono state utilizzate carte di altri produttori, lastre di rame autoincise e lavorate da suo padre.Uno dei punti salienti della cartografia seicentesca è la mappa murale a più pagine. Ne è un esempio - del 1656 - la carta della Zelanda: “Zelandiae Comitatus novissima Tabula”. Questo consisteva in nove fogli che insieme avevano una dimensione di 140 x 160 cm. Aggiungendo paesaggi urbani, la mappa potrebbe essere ulteriormente ingrandita. Questi paesaggi urbani furono a loro volta pubblicati intorno al 1668 con il nome: “Speculum Zelandiae”.
Sei interessato ad acquistare questa opera d'arte?
Artwork details
Related artworks
- 1 - 4 / 4
- 1 - 4 / 24
- 1 - 4 / 12