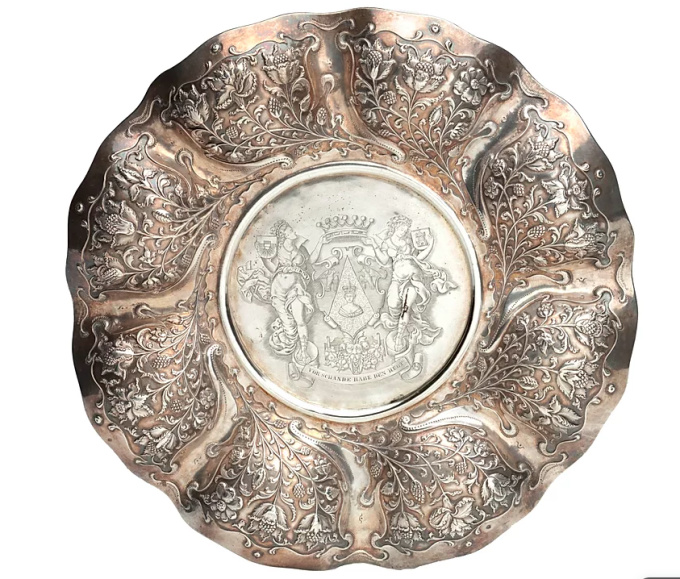
UN PLAT EN ARGENT LOBBED INDONÉSIEN INSOLITE late 17th
Artiste Inconnu
Argent
Prix sur demande
Zebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
- Sur l'oeuvre d'artAN UNUSUAL INDONESIAN LOBBED SILVER DISH
Jakarta (Batavia) or Coromandel coast, third quarter 17th century, apparently unmarked
The eight lobbed dish exuberantly decorated with floral motifs, with the middle section replaced, consisting of indistinctly marked German silver from the early 19th century, bearing the coat-of-arms of the Von Pfeffel family.
Diam. 30.5 cm
Weight 461 grams
Note:
Lobbed silver dishes with exuberant floral decorations were characteristic of the decorative arts in the Netherlands in the first half of the 17th century. This style of floral decoration was adopted by silversmiths as well as by furniture makers working on the Coromandel Coast and in Batavia, often by workers who had fled the Coromandel Coast because of war and famine. In Batavia this style was known as “Custwerck” (work from the Bengal coast).
These lobbed dishes are seldom marked. Only after 1667 the use of the town mark became obligatory in Batavia but only for silver made in Batavia not for silver imported in Batavia from other VOC settlements. The engraved coat of arms in the centre is a replacement of the original centre.
The coat of arms can be identified as those of Christian Hubert von Pfeffel (1765- 1834). As a diplomat, statesman, ambassador of Bavaria in London and Saxony and councillor to the King of Bavaria, he was made “Freiherr” in 1828 and since then used this coat of arms. His son Karl Maximilian Friederich Hubert Freiherr von Pfeffel (1811-1890) in 1836 married Karoline Adelheid Pauline von Rottenburg (1805-1872), the natural daughter of Prins Paul von Württemberg (1785-1852) and his mistress Margrethe Porth. Paul was the jounger brother of the King Wilhelm I of Württemberg (1781-1864). The heraldic motto of the von Pfeffels Vur Schande habe den Huot means as much as “Beware of Shame”. Christian Hubert Theodoor Marie Karl von Pfeffel Karl Maximilian’s grandson was the last male in the von Pfeffel line. His daughter, Marie Louise (Paris in 1882 - Cornwall 1944), born and grown-up in France, changed her name in de Pfeffel. She was the great grandmother of Boris Alexander de Pfeffel Johnson, the present British Secretary of State. None of the members of the von Pfeffel family had any direct links with the Dutch East Indies but indirectly by way of the Royal House of Württemberg they did.
Sophia Frederika Mathilda von Württemberg (1818-1877), daughter of Wilhelm I King of Württemberg, in 1839 married Willem III of the Netherlands and was Queen from 1849 till her death in 1877. The marriage was a disaster; Willem, known in Holland as “King Gorilla”, had many affairs and Sophie, being intellectually far his superior with much interest in art and culture, was a bit of a hysteric. Sophie was a niece of Prins Paul von Würtemberg and therefore a full cousin of Karoline von Pfeffel, the natural daughter of Paul von Württemberg. Karoline and Sophie were good friends.
In the collection of the Gemeente Museum Den Haag is a beautiful lobbed dish with a border of irrefutable late 17th century oriental origin but with an inserted European silver plaque in the centre showing Queen Sheba’s visit to King Solomon. The maker of this plaque must be sought in the circles around the Augsburg silversmith Johann Andreas Thelot (1655-1734). Although the dish and plaque date from around the same time they have been put together only in the late 19th century. In the late 19th century it was certainly not uncommon to make counterfeits of this kind to “improve”on things from the past, as these two examples show (Silver from Batavia, Titus Eliëns, Gemeentemuseum Den Haag, ill. 4). - Sur l'artiste
Il peut arriver qu'un artiste ou un créateur soit inconnu.
Certaines œuvres ne doivent pas être déterminées par qui elles sont faites ou elles sont faites par (un groupe d') artisans. Les exemples sont des statues de l'Antiquité, des meubles, des miroirs ou des signatures qui ne sont pas claires ou lisibles, mais aussi certaines œuvres ne sont pas signées du tout.
Vous pouvez également trouver la description suivante :
•"Attribué à …." A leur avis probablement une oeuvre de l'artiste, au moins en partie
•« Atelier de …. ou « Atelier de » À leur avis, une œuvre exécutée dans l'atelier ou l'atelier de l'artiste, éventuellement sous sa direction
•« Cercle de… ». A leur avis une oeuvre de la période de l'artiste témoignant de son influence, étroitement associée à l'artiste mais pas forcément son élève
•« Style de … ». ou "Suiveur de ...." Selon eux, une œuvre exécutée dans le style de l'artiste mais pas nécessairement par un élève ; peut être contemporain ou presque contemporain
•« Manière de… ». A leur avis une oeuvre dans le style de l'artiste mais d'une date plus tardive
•"Après …." A leur avis une copie (quelle qu'en soit la date) d'une oeuvre de l'artiste
•« Signé… », « Daté… ». ou « Inscrit » À leur avis, l'œuvre a été signée/datée/inscrite par l'artiste. L'ajout d'un point d'interrogation indique un élément de doute
• "Avec signature ….", "Avec date ….", "Avec inscription …." ou "Porte signature/date/inscription" à leur avis la signature/date/inscription a été ajoutée par quelqu'un d'autre que l'artiste
Êtes-vous intéressé par l'achat de cette oeuvre?
Artwork details
Related artworks
- 1 - 4 / 12
Artiste Inconnu
Japanese transition-style lacquer coffer 1640 - 1650
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Artiste Inconnu
A Surinam-themed Amsterdam long-case clock1746 - 1756
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 Sélectionné par
Sélectionné parGallerease Magazine
Artiste Inconnu
A silver spoon commemorating Juff’ Margareta van Hoorn1656 - 1694
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Paulus Franciscus Kromjong
Fleurs devant Arearea Aka (joie) par Gauguin '20th century
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Artiste Inconnu
A Dutch colonial Indonesian betel box with gold mounts1750 - 1800
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 24Shiba Kokan
Peinture d'un hollandais fantastiqueearly 19th
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 Sélectionné par
Sélectionné parDanny Bree
Artiste Inconnu
Deux portraits d'étude du Mas Marco Kartodikromo1900 - 1950
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Cornelis Anthonisz Theunissen
TRÈS RARE PREMIÈRE CARTE IMPRIMÉE D'AMSTERDAM, VILLE EN ASCENSION1544
€ 175.000Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De Jonge
 Sélectionné par
Sélectionné parDanny Bree
1 - 4 / 24- 1 - 4 / 24
HUGO VILFRED VON PEDERSEN
Gadesanger fra Singapore (Musician from Singapore)1870 - 1959
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Artiste Inconnu
A rare Japanese export lacquer medical instrument box1650 - 1700
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Abraham Salm
Twenty-four chromolithographs of Java after A. Salm”1801 - 1876
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Artiste Inconnu
A large Japanese Imari porcelain 'VOC Groningen' dish1800 - 1925
Prix sur demandeZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 12